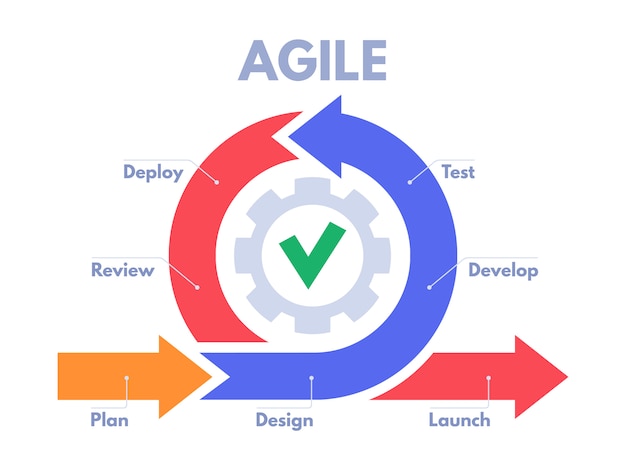
First of all, let’s go through the high-level definition of Agile Methodology.
- Agile says that shift the product incrementally every few days instead of waiting for the whole project to get complete & then release.
- Agile has releases on a regular basis.
EPIC AND USER STORY are the two basic terms of Agile Methodology.

EPIC
- Epic is a large work item.
- It cannot be delivered within a single iteration or it’s large enough that it can be split into smaller stories.
USER STORY
- A User Story is the smallest unit of work in an Agile Methodology.
- The purpose of a User Story is to articulate how a piece of work will deliver a particular value back to the customer.
- User Stories are a few sentences in simple language that outlines the desired outcome.
- Requirements are added later, once agreed upon by the team.
- User Stories are often expressed in a simple sentence, structured as follows:
"As a [person], I [want to], [so that]"
This is the syntax in which User Stories are written in Jira.
For Example:
As a [End User/ Customer], I [want to login to the internet banking dashboard] so that [I would be able to make my payment].MAJOR ADVANTAGES OF AGILE METHODOLOGY:
- It improves the quality of the product.
- It allows for Change.
- It has predictable costs and schedules.
- It is more transparent.

CHALLENGES OF AGILE METHODOLOGY:
- Limited Documentation.
- No finite end.
SOFTWARE TESTING LIFE CYCLE (STLC)
- Software Testing is also standardized So, just like the development of Software has a lifecycle, Testing too has a lifecycle.
- Have a look below:

REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS
- It is most important to understand the requirement both for Developers & Testers.
- A meeting is held before kickstarting any project where the requirement of the project is made very clear to the team.
TEST PLANNING
- A test plan is a document that contains the plan related to all testing activities which need to be done to deliver a quality product.
- This document is prepared after analyzing the Business requirements of the project.
- It is generally prepared by the QA lead or Senior QA in the Agile team.
- The focus of the document is to describe:
- What to Test?
- What cannot be Tested?
- The tools that would be used for Testing, Infrastructure required to Test.
- Testing duration.
- Risks & contingencies plan.
TEST CASE DEVELOPMENT
- In this stage, Test cases are prepared keeping in mind the requirements of the client.
- In Agile, Test Cases are prepared module by module.
TEST ENVIRONMENT SETUP
- It is the most crucial aspect of the testing process.
- It includes hardware configuration, operating system settings, software configuration, test terminals, and other support to perform the test.
- Development and QA Servers should not be messed up. Both should be different.
- Development Server has it’s own database & the Test Server has it’s own. In fact, the Testing Server should be faster in order to run test cases smoothly.
TEST EXECUTION
- During this phase, the testers carry out the testing based on the test plans and the test cases prepared.
- Bugs are reported back to the Development team for correction and retesting is done once the bug gets fixed.
- In this stage only, the QA team shows the client how the product is working before its release.
TEST CYCLE CLOSURE
- It’s the final check after the project is Live.
- It is done mostly after the product is delivered.
- It mainly comprises of:-
- Ensuring the Test Completion: To ensure that every test case has run.
- Handing over the Test Artifacts: It includes details such as, which tests have been automated. So that when the project comes to maintenance, it would be helpful.
- Project Retrospectives: It includes discussions on mistakes that should not get repeated in the future. All these are documented.
- Test Plan & Test Work Products.

